7.6.4. Load estimation function
7.6.4. Load estimation function
The load estimation automatically secures the physical values (mass, center of position, inertia) of a tool attached at the front end of the robot through a certain operation. The physical values of the tool attached at the end need be entered to use the robot correctly and safely.
The mass, center of mass and inertia of each link of the robot’s main body is registered in the controller. However, in case of individual tools, the user needs to enter the values because the tools are attached because of the user’s purpose. If the mass and center of gravity of the tool are known already through the CAD data, the values can be entered directly by the user. The mass (kg), center and inertia of the tool can be entered ‘『[F2]: System』 →『3: Robot parameter』 → 『1: Tool data』’.
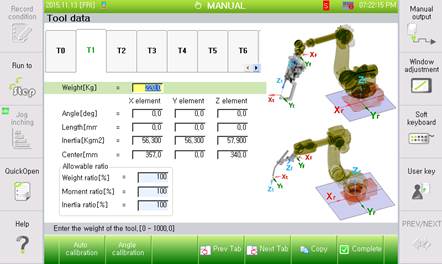
Figure 7.95 Tool data setting screen
Individual items regarding the tool data are as shown below.
n Weight (Unit: Kg): Indicates the total weight of the tool mounted at the end of the robot.
n Inertia (Unit: Kg∙m2): Indicates the inertia momentum of the tool. It will be determined by the distribution of mass around the circumference of X, Y, and Z axes based on the center of gravity. The more distant the mass of a load is distributed from the rotation axis, the higher the value will get.
n Center (Unit: mm): Indicates the distance in the x, y, and z directions from the center of the robot flange surface to the center of gravity of the tool. It is measured in the unit of mm.
n Tool data coordinate: The inertia and the center are to be displayed in the values in the X, Y, and Z directions as shown in “Figure 7.96 Tool Data”.
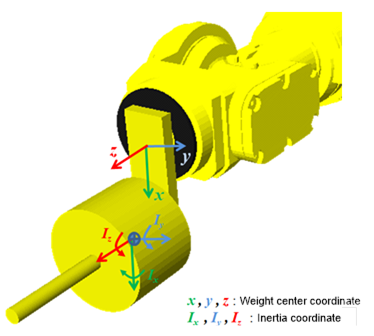
Figure 7.96 Tool data
However, in general, it is not easy to secure the weight, inertia and center of gravity of a tool from the CAD data. That is why the load estimation function is used to calculate the physical values of a tool automatically from the robot controller.
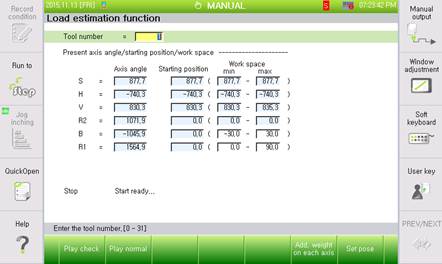
Figure 7.97 Load estimation function screen
The procedure of the load estimation function is as shown below.
① Selection of the load estimation function
② Each axis’ additional weight input
- Additional weight refers to all types of devices that the user installs to the robot, such as welding dressing devices and welding signal line relay box, but not including the tools that are installed at the front end of the robot.
- The load estimation function calculates only the physical values of the tools installed at the front end of the robot.
- If the load estimation function is performed when additional weights are applied, all other weights installed on the robot are considered as weights on the front end.
- Thus, it is necessary to input the additional weight information by selecting 『[F6]: Additional weight of each axis』 for accurate load estimation.
③ Main axis posture designation
- In the load estimation menu, it is possible to operate the robot’s main axis to move the robot to an area where the load estimation operation can be performed safely.
- After moving the robot to a safe area where load estimation can be performed, select 『[F7]: Set pose』.
④ Wrist axis operation area input
- The user can designate the operation area of the wrist axis that is to be used in the load estimation operation. With this function, it is possible to perform load estimation in an operation area where there is no interference with adjacent facilities or the robot main body.
(※ This function may not be supported in some robots.)
⑤ Check operation
- In order to check for any interference with adjacent facilities or the robot main body during the load estimation process, operate the robot at low speeds by selecting 『[F1]: Check operation』.
⑥ Tool number input and normal operation
- Set the tool number that needs to be used and select 『[F2]: Play normal』 to perform load estimation.
⑦ Estimation result reflection
- Check the estimation result and select 『[F7]: End』 to register the result of the load estimation into the defined tool number.
For more details, refer to 『Hi5a Controller “Load Estimation” Function Manual』.
l It may be impossible to perform load estimation depending on the condition of the wrist axis operation area.
l In some robots, it may be impossible to designate the condition of the wrist axis operation area.