4.8.2. Error logging
4.8.2. Error logging
History of error and warning is indicated. When an error occurs, details, time, program number, step number, axis data and input/output state can be checked. The content of errors can be recorded to manage the history of errors. History can be initialized by pressing 『[F1]: Remake』key. Cause of error and restoration work can be precisely determined by referring to history.
(1) Selection 『[F1]: Service』 → 『7: System diagnosis』 → 『2: Error logging』.
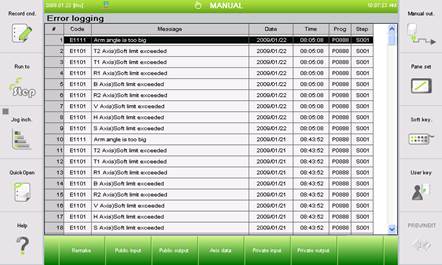
Figure 4.140 Error logging screen
(2) When you select a specific error item, and click on one of 『[F2]: Public input』, 『[F3]: Public output』, 『[F4]: Axis data』,『[F5]: Private input』, 『[F6]: Private output』, you can check the status in case of an error. For example, if you select 『9: E0016 Servo drive error』with the arrow key and press the 『[F5]: Private input』key, the following screen will be displayed.
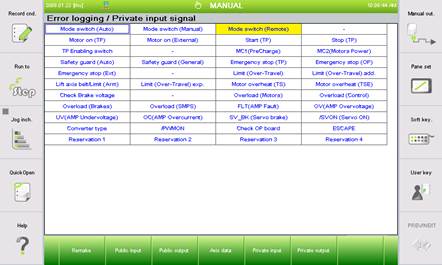
Figure 4.141 Error logging/private input signals
l Pressing the『[F1]: Remake』key allows the user to enter the maximum count of logging.
l The Error record basically holds up to 100 error histories. However, the number of error histories can be set within the range of 1~1000 depending on the needs of the user. When the user enters the maximum number of histories and press the [Enter], all the histories saved up to now will be deleted, making it possible to save the error histories in the number set by the user.