7.6.4.3. Inertia
7.6.4.3. Inertia
This refers to the inertia momentum of the load. Assuming that it rotates in x, y and z direction, it is the sum of square value of the mass distributed in the load and distance from the rotating axis.
Inertia is decided by the mass distribution around the axis and the farther away from the axis, the bigger the inertia.
Kgm2 unit is used for x, y and z axis.
For example, the methods calculating the inertia for the parallelepiped and cylinder shapes, shown below, are as follows.
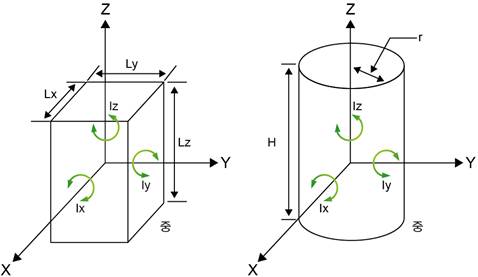
Figure 7.64 Inertia calculation for cube tool Figure7.65 Inertia calculation for cylinder tool
Unit: Weight [㎏], Length [m], Inertia [㎏㎡]