2.1.2.1. Methods of Setting a Cube
2.1.2.1. Methods of Setting a Cube
Two methods of setting a cube are provided
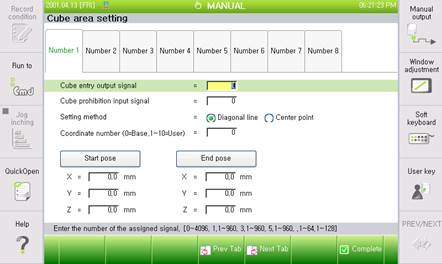
(1) Diagonal Method
n Set up hexahedron’s two points, located diagonally as diagonal points. Manually input the diagonal starting and terminal positions as seen in the following figure.
n If recording the current robot’s position as a TCP, put a cursor on the <Start Pose> or <End Pose> button, and press the ‘ENTER’ key.
Example)
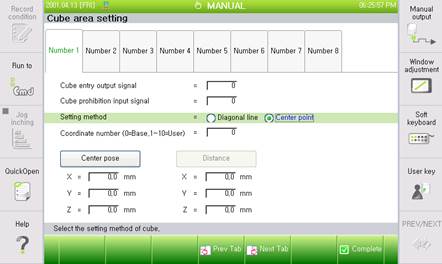
(2) Method of Setting a Center Point
n The method of setting a Center Point is to establish the cube’s Center Point and each distance in the X, Y, and Z directions, respectively.
n If recording the current robot’s position as a Center Point, put a cursor on the <Central Position> button and press the ‘ENTER’ key.
Example)
(3) Setting a Cube in the User Coordinate System
n The cube area is created in the shape of a rectangular parallelepiped. So, if the user coordinate system is used in setting the cube, cube areas with various positions in space may be created.
n As seen in the following figures, several cubes may be established: cube 1 is set in the base coordinate system; cube 2, the user coordinate system; and cube 3, the user coordinate system 2.
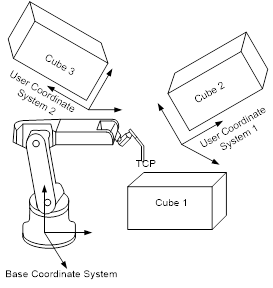
n When the user coordinate system is used in setting the cube, the diagonal and central positions shall be created in the user coordinate system.