10.5.3.5. SEA
10.5.3.5. SEA
The search function is for detecting the difference of workpiece position and compensating the difference. Not only robot coordinates system but also tool coordinates system and base coordinates system can be used as the standard to detect and compensate the position difference. This command is used when the moving robot is stopped by the detection signal and its position is compared with the reference position to calculate the shift amount. The calculated shift amount through this method by using the online shift command can be applied to changing existing work areas en bloc. You can get the search and operation function that you want when you use this command in conjunction with the RINT/RINTA, SONL commands. Also, setting the search reference position and the range must be set in the 『[F7]: condition setting』 à 『[F1]: App. cnd』 menu.
Explanation | Search function | ||
Syntax | SEA ST=<On/Off>, CRD=<Reference coordinate>[,<User coordinate number>], R=<register number> | ||
Parameter | On/Off | If 1, on. If 0, off. | 0~1 |
Reference coordinate | 0=Base, 1=Robot, 2=Tool, 3=User, 4=User n | 0~4 | |
User coordinate number | User coordinate number when reference coordinate is used | 0,1~10 | |
Register number | Number to be used for online shift | 1~8 | |
Example | SEA ST=1,RF=0,R=1 | ||
(1) Assign search range. (From 『[F7]: Condition setting』 menu 『[F1]: App. cnd』 → 『2: Robot search range』) If you move and search from step 2 to step 3, the range is shown in the following figure.
(2) Perform program teaching and set the search function for teaching.
① Add a search start command (ST=1)
② Robot interrupt (RINT or RINTA) (Setting of the interrupt input signal , RC = 1 input)
X, Y, and Z are not required to be set because they are automatically updated when the search reference position is recorded.
③ Moving step recording of a robot
④ Add a search end command (ST=0).
⑤ Add online shift.
⑥ Perform a work where shift is required.
⑦ End online shift.
(3) Set search standard position record ‘ON.’ From 『[F7]: Condition setting』 menu 『[F1]: App. cnd』 → 『1: Robot search ref. pose record』)
(4) Operate the program in the 1Cycle Mode to retrieve the standard position of workpiece through robot interrupt.
The position value is recorded in the X, Y, and Z entries of the RINT/RINTA commands, which were previously executed.
(5) Set search standard position data record ‘OFF.’ From 『[F7]: Condition setting』 menu 『[F1]: App. cnd』 → 『1: Robot search ref. pose record』)
(6) Operate the program ordinarily.
(7) It runs the task with shifting by the difference between the detected interrupt position and reference position.
l The search section must be moved to the linear interpolation operation, which enables accurate position detection.
l Application of the search function
① One-dimension search
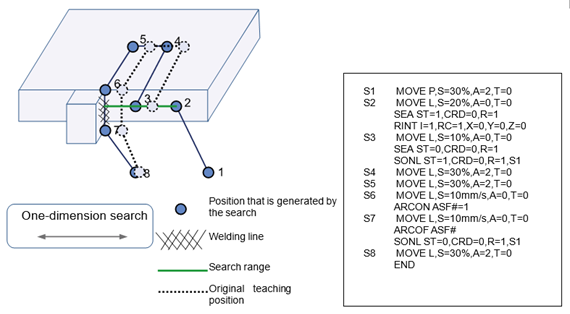
Figure 10.8One-dimension Search
Figure 10.8 shows the error is corrected by one-dimension search when workpieces of the same kind or of the same shape and different size move.
The search function is used with robot interrupt as shown above. The difference in shift amount is corrected by the online shift function after the amount is recorded in shift register.
Search function begins to be executed through a SEA command after moving to the step no. 2 position. X, Y, and Z values of the RINT command in the figure above are updated to the actual interrupted position when the search reference position is recorded.
While moving to the step no. 3 position, it detects the range set to “Robot search range.” When the interrupt signal is input, it assigns the shift amount to the register after generating shift amount by assigning values to the X, Y, and Z items of the RINT commands (when the reference position recording mode is ON) or when comparing them to X, Y, and Z items. (When the reference position recording mode is OFF)
Refer to the shift register, which works by shifting the step 4 – step 7 programs.
② Two-dimension search
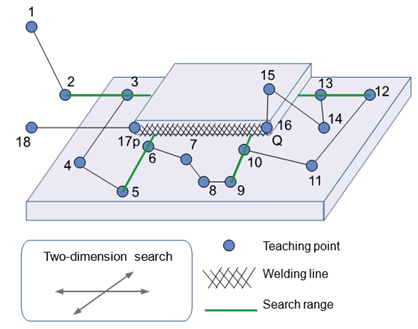
Figure 10.9Two-dimension search
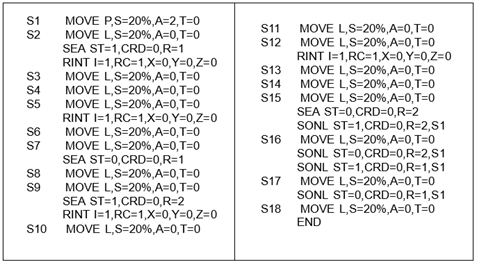
Two-dimension search records shift amounts of each point (P and Q) by using the search function twice. The shift amount of point P is stored in R1 register and referred to when P is shifted. The shift amount of point Q is stored in R2 register and referred to when Q is shifted.